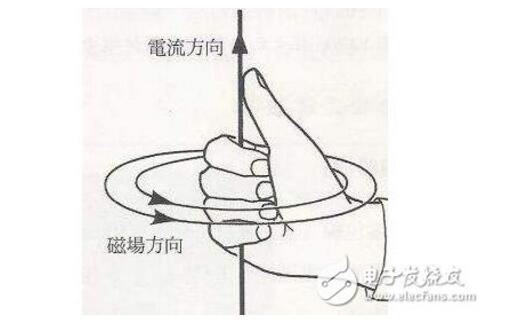
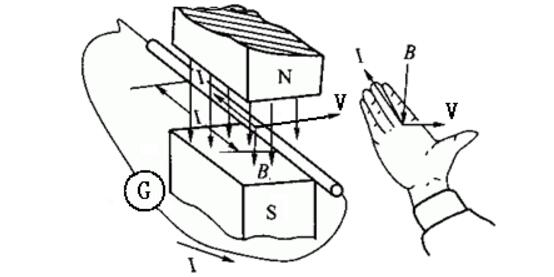
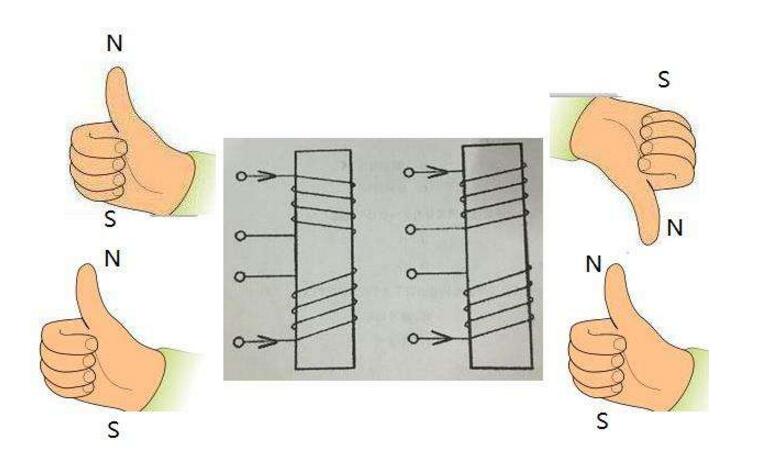
The direction of the electromotive force in the law of electromagnetic induction can be determined by Lenz's law or right-hand rule. Right hand rule content: Stretch the right hand so that the thumb is perpendicular to the four fingers, the palm is toward the N pole of the magnetic field, the direction of the thumb is consistent with the direction of the conductor movement, and the direction indicated by the four fingers is the direction of the induced current in the conductor (induced electromotive force) The direction is the same as the direction of the induced current). Lenz's law states that the magnetic field of the induced current obstructs the change of the original magnetic flux. In short, the magnetic flux becomes larger, and the generated current has a tendency to make it smaller; while the magnetic flux becomes smaller, the generated current has a tendency to make it larger. The "right-hand rule" is also called the generator rule, which is used to determine the direction of the induced electromotive force (inductive current) of a conductor moving in a magnetic field. In electromagnetism, the right-hand rule determines the direction that is not related to force. If it is related to force, it depends on the left hand rule. That is, with regard to the left hand of the force, the other (usually used to judge the direction of the induced current) is determined by the right hand. (This is often mixed, you can find the word "force" to the left, use the left hand; and the "electric" word to the right, use the right hand) memory mouth: left Tongli right electricity. It can also be remembered as: use the left hand due to electricity, and use the right hand because of the movement. The method is brief: the right hand finger is punched in the direction of the current, the thumb is extended, and the direction of the thumb is observed. You can use the direction of the palm of your right hand and the direction of the finger to remember the direction of the current generated when the wire cuts the magnetic induction line, that is, extend the right hand so that the thumb is perpendicular to the other four fingers, and both are in the same plane as the palm; The sense line enters from the palm of the hand and points the thumb at the direction of the wire movement. At this time, the direction indicated by the four fingers is the direction of the induced current. This is the right-hand rule for determining the direction of the induced current when the wire cuts the magnetic induction line. The right-hand rule determines the relationship between the coil current and the direction of the magnetic induction line and the relationship between the current direction of the conductor cutting magnetic line and the direction of the conductor movement. The force df12 of the current element I1dι to another current element I2dι separated by γ12 is: μ0I1I2dι2&TImes;(dι1&TImes;γ12) Df12=────────────── 4πγ123 In the formula, the direction of dι1.dι2 is the direction of the current; γ12 is the radial vector from I1dι to I2dι. Ampere's law can be divided into two parts. One is that the magnetic field generated by the current element Idι (ie, I1dι above) at γ (ie, γ12 above) is μ0Idι&TImes;γ dB=─────── 4πγ3 This is Bi-Sa-La law. The second is that the current force Id1 (ie, the above I2dι2) is subjected to the force df (ie, the above df12) in the magnetic field B is: Df=Idι&TImes;B The right hand is flat, so that the thumb is perpendicular to the rest of the four fingers, and both are in the same plane as the palm. Put the right hand into the magnetic field. If the magnetic induction line enters the palm of the hand vertically (when the magnetic induction line is straight, it is equivalent to the palm facing the N pole), and the thumb points to the direction of the wire movement, then the direction indicated by the four fingers is the induced current in the wire ( The direction of the dynamic electromotive force). Generally know any two of the magnetic field, current direction, and direction of motion, let you judge the third direction. (This section is taught in Physical Education Elective 3-2, mentioned in the first unit) Right-handed screw rule: (ie, Ampere's rule) Hold the solenoid with the right hand, and bend the four fingers to the same direction as the current of the solenoid. The end pointed by the thumb is the N pole of the magnetic field generated by the energizing solenoid. . In the case of a linear current magnetic field, the thumb points to the direction of the current, and the direction of the four-finger bending finger is the direction of the magnetic induction line (the direction of the magnetic field is either the direction indicated by the north pole of the small magnetic needle or the direction of the small magnetic needle). When applying the right-hand rule, the object should be a straight wire (of course, it can also be used to energize the solenoid), and the velocity v and the magnetic field B should be perpendicular to the wire, and v and B should be perpendicular. The right-hand rule can be used to determine the direction of the induced electromotive force, such as the right-hand generator rule to determine the direction of the induced electromotive force of the three-phase asynchronous motor rotor. The reason for generating the right-hand rule is that the three-dimensional, right-hand rule of electricity, magnetism, and mass represents the electrical dimension, magnetic dimension, and quality information gradient dimension. On the question of distinguishing between the right-hand rule and the left-hand rule, there is a four-character slogan: left-right and right-handed. See left hand rule and right hand rule. The rule for determining the direction of induced current in a wire moving in an external magnetic field is also called the motor rule. It is also a rule for determining the relationship between the direction of the induced current, the direction of movement of the conductor, and the direction of the magnetic field lines. The flat hand is applied to the direction of the magnetic field of the generator palm, the thumb is the direction of motion of the object, and the finger is the direction of the current, and the rule of the direction of the moving electromotive force generated in the conductor when the magnetic line of the conductor is cut is determined. The content of the right hand rule is: stretch the right hand, make the thumb perpendicular to the other four fingers and both in the palm of the plane, put the right hand into the magnetic field, let the magnetic line penetrate vertically into the palm, and the thumb points to the conductor movement. In the direction, the remaining four fingers point in the direction of the moving electromotive force. The direction of the electromotive force is the same as the direction of the induced current generated. The direction of the dynamic electromotive force determined by the right-hand rule conforms to the law of energy conversion and conservation. The right-hand rule can also be considered a special case of Lenz's law. In the rigid body rotation law, the direction of the moment obeys the right hand rule, that is, the four fingers are surrounded by the direction of r from the direction of r to the direction of F, and the direction represented by the thumb is the direction of the moment. We provide quick-turn injection molding by many types of materials, like ABS, PA66, PBT, TPU, TPE, PVC, PE, NYLON 6, PC, silicone, TPE, EPDM, PUR, etc. Special for some plastic parts. Our advantages in internal prototyping, bridge tooling and short-run manufacturing, which can eliminate the costly and time-consuming for customers a lot.
ETOP experienced to support one-stop cable assembly solution service, including wire harness, palstic enclosure, silicone, metal, PCBA, etc.
Injection Molding Parts,Plastic Injection Molding,Low Cost Plastic Injection Molding,Plastic Mold Injection Molding ETOP WIREHARNESS LIMITED , https://www.oemwireharness.com