The main application technology of the Internet of Things technology in the field of medical and health lies in three aspects of material management visualization technology, medical information digital technology, and medical process digital technology. (1) Monitoring and management of medical devices and drugs With the aid of the visualization technology of material management, the production, distribution, anti-counterfeiting and tracing of medical devices and medicines can be realized, to avoid public medical safety issues, and to achieve full-scale real-time monitoring of medical devices and drugs from scientific research, production, flow to use. Traditional RFID technology is widely used in asset management and device tracking applications. People hope to strengthen the application of this technology in drug tracking and device tracking through legislation. According to the report of the World Health Organization, the proportion of counterfeit medicines in the world has exceeded 10%, with sales exceeding 32 billion yuan. Relevant data from the Chinese Pharmaceutical Association show that at least 200,000 people die each year from the wrong medication and improper medication, and 11% to 26% of the unqualified medication users. And about 10% of cases of medication errors. Therefore, RFID technology plays an important role in tracking and monitoring medicines and equipment, and rectifying and regulating the market of medical supplies. According to the report of "Global Healthcare and Pharmaceutical Application Market", the revenue of RFID in the healthcare and pharmaceutical application market in 2011 will grow to US $ 2.318 billion, with a compound annual growth rate of 29.9%. Among them, the compound annual growth rate of the drug tracking market will be close to 32.8%, and the compound annual growth rate of the medical device tracking market will reach 28.9%.   Specifically, the application direction of the Internet of Things technology in the field of material management has the following aspects: 1. Anti-counterfeiting of medical equipment and medicines. The identification label attached to the product is unique and difficult to copy. It can play a role in querying information and preventing counterfeiting and counterfeiting. It will be a very important measure for counterfeit and shoddy products. For example, by transferring drug information to a public database, patients or hospitals can check the contents of the label and the records in the database to easily identify counterfeit drugs. 2. Real-time monitoring throughout. From the scientific research, production, circulation and use of medicines, RFID tags can be monitored in all directions. Especially when leaving the factory, when the product is automatically packaged by itself, the reader installed on the production line can automatically identify the information of each drug and transmit it to the database. During the circulation process, it can record intermediate information at any time and implement full-line monitoring. Through the monitoring of environmental conditions for drug delivery and storage, transportation and monitoring of environmental conditions can be achieved. Ensure the quality of medicines. When a problem occurs, the entire process can be traced back based on the drug name, variety, place of origin, batch, and production, processing, transportation, storage, and sales. 3. Medical waste information management. Through the cooperation of different hospitals and transportation companies, a traceable medical waste tracking system is established with the help of RFID technology to realize the full tracking of medical waste delivered to the treatment plant, and to avoid the illegal treatment of medical waste. At present, Japan has launched research in this area and achieved good results. (2) Digital hospital The Internet of Things has broad application prospects in medical information management. At present, the demand for medical information management in hospitals is mainly concentrated in the following aspects: identification, sample identification, and medical record identification. Among them, identification mainly includes patient identification, doctor identification, sample identification includes drug identification, medical device identification, laboratory identification, etc., and medical record identification includes medical condition identification, sign identification, etc. The specific application is divided into the following aspects: 1. Patient information management. The patient ’s family medical history, past medical history, various examinations, treatment records, drug allergies and other electronic health records can help doctors formulate treatment plans; doctors and nurses can achieve real-time monitoring information on patient vital signs, treatment chemotherapy, etc. Eliminate the phenomenon of wrong medicine, wrong injection, etc., and automatically remind nurses to do medicine distribution and inspection. 2. Medical emergency management. Under special circumstances, such as many wounded people, unable to get in touch with family members, critically ill patients, etc., with the help of reliable and efficient information storage and inspection methods of RFID technology, the patient's identity can be quickly confirmed, and his name, age, blood type, emergency contact number, Relevant detailed information such as previous medical history, family members, etc., completed the admission registration procedures, and won valuable time for the treatment of first-aid patients. At present, the technology has been applied in the wellford hall treatment center in the United States. 3. Medicine storage. Apply RFI D technology in the storage, use and inspection process of medicines, simplify the manual and paper record processing, prevent out of stock and facilitate the recall of medicines, avoid confusion between similar medicine names, doses and dosage forms, and strengthen medicine management To ensure the timely and ready supply of medicines. 4. Blood information management. The application of RFID technology to blood management can effectively avoid the shortcomings of small barcode capacity, can realize non-contact identification, reduce blood pollution, achieve multi-target identification, and improve data collection efficiency. 5. Mistake prevention of pharmaceutical preparations. By adding an error prevention mechanism in the process of taking medicines and dispensing medicines, it is realized in the aspects of prescription issuance, preparation, nursing administration, patient medication, drug effect tracking, drug inventory management, drug supplier purchase, shelf life and environmental conditions Informative management of pharmaceutical preparations, confirm the types of preparations used by patients, record the flow of patients and save batch numbers, etc., to avoid negligence of medications, and safe use of medications by patients. 6. Medical device and drug traceability. Accurately record items and patient identities, including basic information on product use, specific product information related to adverse events, areas where the same quality problem product may occur, patients involved in the problem product, and location of problem product that has not been used, Trace back to bad products and related patients, control all unused medical devices and drugs, and provide strong support for accident handling. In 2007, China first experimented with the establishment of a traceability system for the direct association of implantable medical devices with patients. The system uses GSI standards to identify medical devices and is widely used in hospitals in Shanghai. 7. Information sharing and interconnection. Through the sharing and interconnection of medical information and records, integrate and form a well-developed comprehensive medical network. On the one hand, authorized doctors can review the patient's medical history, patient history, treatment measures, and insurance details. Patients can also choose or change doctors and hospitals on their own; on the other hand, they support township and community hospitals to seamlessly connect with central hospitals in information, and can obtain expert advice, arrange referrals and receive training in real time. 8. Anti-theft system for newborns. Combining maternal and infant identification management, baby anti-theft management, and channel authority in the gynecology and obstetrics and gynecology hospitals of large general hospitals to prevent outsiders from entering and leaving at will, and adopting a practical and reliable protection against mistaking for babies. 9. Alarm system. Through real-time monitoring and tracking of hospital medical equipment and patients, help patients send emergency distress signals, prevent patients from running away privately, prevent damage or theft of valuable devices, and protect temperature-sensitive drugs and laboratory samples. (3) Telemedicine monitoring Remote medical monitoring mainly uses the Internet of Things technology to build a patient-centric remote consultation and continuous monitoring service system based on critically ill patients. The original intention of remote medical monitoring technology is to reduce the number of patients entering hospitals and clinics. According to a 2005 report by the US Centers for Disease Control (CDC), about 50% of Americans suffer from at least one chronic disease, and their treatment costs account for more than three-quarters of the US $ 2 trillion in medical expenditure. In addition to the high cost of high-tech treatment and surgery, doctors ’routine examinations, laboratory tests, and other monitoring services cost about billions of dollars. With the advancement of telemedicine technology, high-precision and sophisticated sensors have been able to achieve effective mutual trust within the body-area of ​​patients, and the focus of telemedicine monitoring has gradually shifted from improving lifestyles to providing timely life-saving information. 3. Current medical technology a. Related technologies mainly include: ultra-low power DSP designed for biomedical signal analysis, low sampling rate / high resolution ADC, low power consumption / ultra-wideband radio frequency, and MEMS energy harvester. 1. Transmit the relevant health information of rural and community residents to the rear through wireless and video, establish personal medical files, improve the quality of primary medical services; allow doctors to conduct virtual consultations, provide intellectual support for large hospitals and large experts for basic hospitals, will The extension of high-quality medical resources to primary-level medical institutions; the construction of a remote continuing education service system for clinical cases, etc., to improve the quality of continuing education for medical personnel in primary-level hospitals. 2. Mobile healthcare. By monitoring some vital signs such as body temperature, heartbeat, etc., a physical condition including the person ’s weight, cholesterol content, fat content, protein content and other information is established for each customer, real-time analysis of human health status, and feedback of physiological index data to the community, Caregivers or related medical units can promptly provide customers with advice on diet adjustment and medical care, and can also provide scientific data for hospitals and research institutes.
As a single sided PCB manufacturer, Jinghongyi PCB has been single sided PCB for many years. Production and manufacturing experience, with a very exquisite single sided PCB Manufacturing process flow chart.
Basically, there is no challenge for PCB manufacturer to produce single sided PCB and the technology is quite mature nowadays. The main focus for PCB manufacturer is how to control production cost and save more cost for customers.
It is the type of a single layer PCB which is made up a rigid material such as fiber glass. These PCBs are inflexible and prevent the circuit from bending and breaking. Currently these are used in different types of devices such as in calculators and power supplies etc.
It is the type of a single layer PCB which is mode out a flexible material instead of a rigid material and for this purpose plastic materials are used. It has so many advantages over single layer rigid pub but it fabrication cost is so much high.
It is the type of a single layer PCBs which is used for high frequency circuits normally in giga hertz. These PCBs are made out a Teflon or polyphenylene oxide (PPO) material. During choosing high frequency single layer PCB many aspects are keep in mind such as dielectric loss, thermal expansion and water absorption etc.
It the type of single layer PCBs which is made out by the combination of plastic and fiber glass. Both materials are combined together into single layer. It has so many advantages over single layer rigid and flexible PCB such as it reduces the weight and size of overall PCB.
single sided vs double sided PCB
Single Sided PCB Single Sided PCB, Single Layer PCB, 1 Layer PCB, making circuit boards JingHongYi PCB (HK) Co., Limited , https://www.pcbjhy.com
The Single Most Important Thing You Need To Know About Single Sided PCB
We can produce single sided copper PCB, single sided copper clad PCB Board , single sided Flex PCB .
We know that when you choose single sided PCB manufacturer, product quality is one of the first factors you need to consider. We are not only engaged in PCB manufacturing for many years, but also one of the large-scale PCB manufacturers in China. We can not only produce single sided PCB, but also Double Sided PCB , Multilayer PCB , Aluminum PCB and so on.
In addition to product quality, you may also need to consider the single sided PCB price factor. If you choose us as your partner, you can rest assured that we will be able to provide you with not the best price on the premise of guaranteeing product quality, but the price that we both feel is very reasonable. What do you think?
In this article, we will elaborate on the definition, type, cost components, structure, advantages and disadvantages, manufacturing process and raw materials of single sided PCB. Finally, we will introduce the application of single sided PCB and the differences between single sided PCB and double sided PCB. And how to choose between single sided PCB and double sided PCB.
What Is Single Sided PCB

Single-sided PCB diagram mainly used Network Printing(Screen Printing), that is, resist on copper surface, After etching, mark the welding resistance, and then finish the hole and the shape of the part by punching.
Fundamentally, single-sided and double-sided Printed Circuit Boards serve the same purpose. Both serve as catalysts for electrical connections between components, however there are some key differences that set them apart from each other. More specifically, they differ in the costs associated with production and development processes, as well as ampacity differences.
With the appearance of electronic transistor, single sided PCB was developed in the early of 1950, which is mainly manufactured in USA. Single-sided PCB was manufactured by copper etching directly at that time. During 1953 to 1955, Japan use imported copper make out paper phenolic aldehyde copper substrate, and apply mainly on radio products. In 1956, single-sided PCB technology was made big progress with the appearance of professional PCB manufacturers from Japan. In the early stage, copper substrate mainly used paper phenolic aldehyde, but because paper phenolic aldehyde with the factors of low electric insulation, bad solder thermal stability, twist issue etc, paper epoxide resin and glass fiber epoxy resin was developed soon after. Currently, paper epoxide resin is widely used in consuming electronic.
Types of Single Layer PCB
It the type of single layer PCB which is made out with aluminum material substrate. The design of this PCB is almost same as copper backed PCB but only difference is that, in these PCBs aluminum substrate is used instead of copper. Aluminum backed is used with thermal insulating material for transferring the heat from insulating material to back.
What Goes Into Determining single sided PCB Costs and price
No matter whether manufacturing a single-sided PCB, double-sided PCB, or multilayer PCB, three main cost categories exist: Primary production costs, dependent costs, and overhead costs.
Often, single layer PCB are used for simple devices and usually cheaper than multilayer PCB.
Multilayer PCB has one or multiple conductor patterns inside the board, this increases the area available for wiring. multilayer PCB, such as 4 Layer PCB , 6 Layer PCB and 8 Layer PCB are usually used for more complicated devices. For example, smart phones use 12 layers due to the various demands of the circuit. As a result, multilayer PCB circuit boards are more expensive.
You can break them down into the following categories:
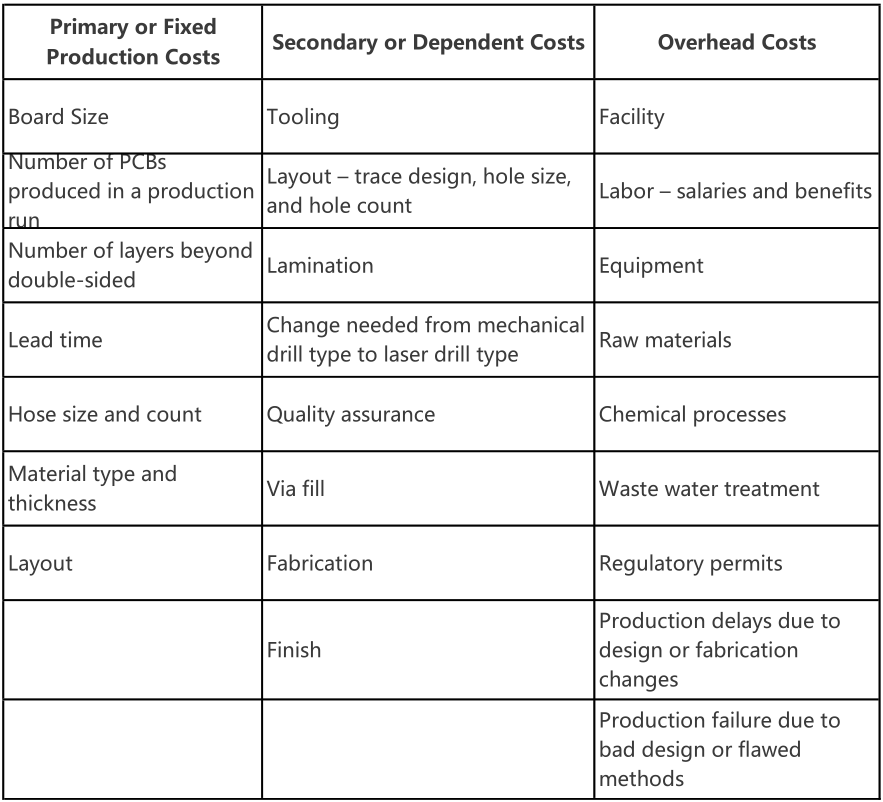
Layout alters the cost balance. While the number and size of holes remain the same with single-sided PCBs, two different circuit designs on one substrate change the number of holes and add vias.
Because double-sided PCBs welcome complex circuit designs, layout also becomes a dependent factor. As the number of traces increase, costs increase. Smaller surface mount components fastened to the bottom side change the trace spacing. As the space between the traces narrows, costs can jump 5 to 10 percent.
Different layouts may require different hole sizes and the use of laser rather than mechanical drills. Smaller hole sizes and larger hole counts drive the cost higher because of a change in the manufacturing process.
Advantages of Single Sided PCB

Single Layer PCB Disadvantages
Despite their cost advantages and other perks, single-layer boards are not the right choice for every project due to the limitations they have, which include:
How to make single sided PCB

Single sided PCB manufacturing Process flow chart
One thin layer of thermally conductive but electrically insulating dielectric is laminated with copper. Soldermask is usually applied on top of the copper.
Cutting - Cleaning - Drilling - Cleaning - PTH - Panel - Plating - Cleaning - Photolithography - Image Transfer - Inspection - Copper/Tin - Plating - Coating - Removing/Etching/Tin - Removing - Inspection - Cleaning - Solder - Mask - Exposure/Develop/Inspection - Prepreg - Screen - HASL - Conformal - Coating - Post - Soldering - Cleaning - Test - Final Inspection - Packing
Single layer PCB Raw Material
Construction of Single Sided PCB
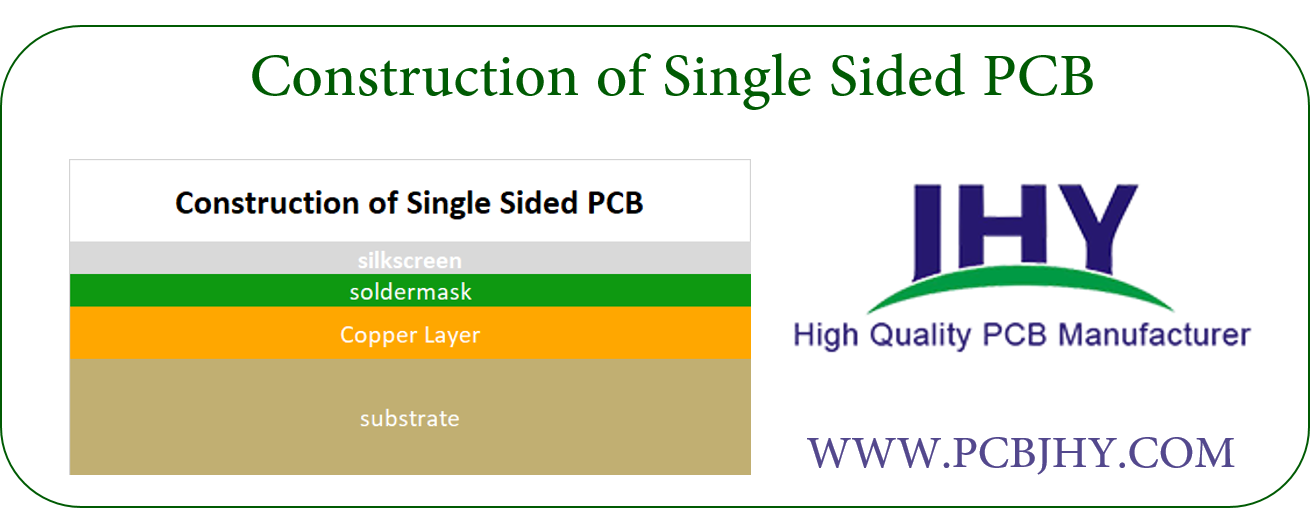
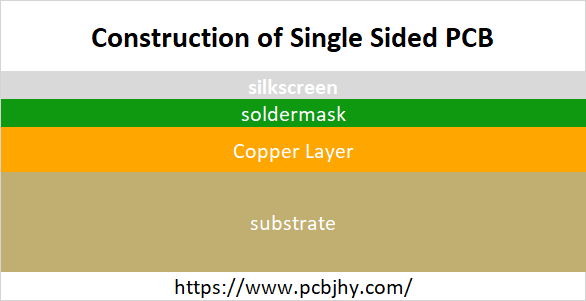
The base material, which is also named as substrate, is composed of insulating fiber glass which gives PCB strength and compact look. The nature and type of base material defines if board is going to be Flexible PCB or Rigid PCB.
Above substrate, there lies a copper layer which provides conducting path for various components on the board. The copper thickness is different for different boards depending on your needs and requirements and is defined in ounces per square foot.
On the top of copper foil, there exists a solder mask layer. This layer is mainly used for protection and makes the copper foil insulating which helps in avoiding the conduction in case direct contact happens with some conducting material.
On the top of all layers, there exists a silkscreen layer that is mainly used for adding symbols and characters on the board so a common person can anticipate the clear understanding of the board.
Single Sided PCB Applications
What Is Double Sided PCB
It need circuits on both sides. Via is the holes on boards, coated with metal and it can connect wires on both sides. Because the area of Double-sided PCB is twice as large as the Single-sided PCB, and because the wiring is interleaved, which is better suited for circuits that are more complex.
Someone may feel confused that if one Double-sided PCB, wires on both sides while Electronic parts only one side, is this a Double-sided board or a single onel? The answer is obvious. This kind of board is a Double-sided board, it's just install a component on the Double-sided board.
Differences Between Single sided PCB and Double sided PCB

Single and double sided printed circuit boards share the same material make-up: FR-4, which is a form of fiberglass mixed with epoxy. In modern manufacturing, this is usually layered with copper for conductivity and then coated in solder mask for a professional finish. Sometimes, in a process called silk screening, industrial printers print markings and labels on the board as well.
Single-sided PCBs consist of the FR4 insulating core substrate and a thin layer of copper coating on the bottom or solder-side of the substrate. Through-hole components mount on the top or component-side of the substrate with the leads passing through to the bottom side and soldered to the copper pads and tracks. Surface mount components mount directly to the solder side. The primary difference between the two boards will be in conductor placement.
Double-sided boards rely on the same core substrate but have conductors on both sides of the substrate. Very simply, a double-sided board delivers twice the area for conductors. Complex routing can occur with through-hole components mounted on the top layer and surface mount components mounted on the bottom layer. Plated through holes establish [vias" or the electrical connections between the two sides.
Choose Single Sided PCB or Double Sided PCB?
Which PCB you pick depends on your needs and requirements. Sometimes single sided PCBs are more suitable for project design as compared to double sided PCBs and vice versa.
Before you pick any type of PCB for your project, you must take one thing into consideration that single sided PCB layouts are more difficult to route as compared to double sided PCB, but following are the reasons why you should put an effort for making and picking single sided PCB over other PCBs.
Relationship Resources
Multilayer Metal Core PCB
Single Layer Metal Core PCB
Single Sided Flexible PCB