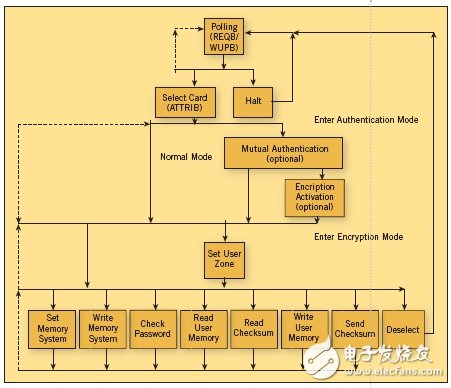
The RFID system generally consists of a single-chip RFID tag and an RFID card reader. The tag integrates a radio frequency front end, memory and controller. The RFID card reader can decode the data on the tag and then perform appropriate operations (such as opening the door). lock). RFID tags are similar to barcodes, but they store product information electronically. In addition to the security features, the latest RFID tags have the ability to automatically update relevant information as the product is transported over the supply chain. RFID tags can be used to track everything from home pets, livestock to high-end electronics. They can automatically collect bridge and road fees and limit access to sensitive areas. Recently, RFID tags have begun to enter more secure areas such as pharmaceuticals, contactless payments, cargo security, and e-passports. These information applications and security-intensive applications must adopt new standards to define RFID tags and readers. Such criteria include the availability of memory on the tag, the robustness of the encryption algorithm, the number of different information areas on the tag, and security. RFID tags must be able to support a more accurate tracking mechanism. Take the pharmaceutical industry as an example. According to the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), the number of counterfeit drugs has increased tenfold in the past five years. In the worst case, fake medicine may even endanger the patient's life. The manufacturer's mark on the tablet can be faithfully reproduced to achieve a false effect. The barcode on the package can provide some additional information and security measures, but it can also be easily scanned and copied. It is estimated that 10% of prescription drugs worldwide are fake drugs, and tens of thousands of lives are lost every year. In order to prevent the spread of counterfeit drugs, Florida states that from July 1, 2006, prescription drugs must have a paper-based medical record, including the name of the drug, the dosage form, concentration, manufacturer, batch number, corresponding invoice/ Shipping/transfer voucher number, transaction date, name and address of each owner, name and address of each drug user, identification certificate, contact information of each wholesaler, confirmation of the drug record information is accurate and complete Sexual signature or oath, as well as information such as the manufacturer's tracking number. California, USA requires that from January 1, 2009, drugs must have electronic drug records, and other states will follow suit. It is very difficult to track so much information for many RFID tags currently on the market, which requires not only a large amount of on-chip memory, but also a plurality of different security areas. For example, the manufacturer's ID, date of manufacture, and product specifications should be readable by everyone, but only the manufacturer can write it; the retailer's ID can be written not only by the distributor, but also at the retail point. Authorized person to update. This type of data and security-intensive applications may require 64Kb of on-chip EEPROM and up to 16 different user areas (Figure 1). Design engineers should be aware of whether the tag vendor provides sufficient storage density and user provisioning capabilities for the application being developed. Most tags have a memory capacity of 2Kb and below, and usually only have two banks. While this storage density is more than adequate for animal tracking applications, it is not sufficient to track the requirements of each receiving link in a complex supply chain. Figure 1: Atmel offers a range of RFID tags, from 64b read-only memory to 64k-bit read/write protected memory, and 4 to 16 memory areas. Security is an important issue for RFID systems, but the security of RFID systems (generally provided by label and tag reader vendors) has not been enough (Figure 2). Most of today's RFID tags use an old encryption algorithm with a 48-bit key that can be cracked in a few hours using a laptop. Figure 2: Schematic diagram of a typical security process for an RFID system. However, the situation has improved. Some RFID vendors have introduced tags and readers that support advanced encryption algorithms with 64-bit keys. From 48-bit keys to 64-bit keys, security performance is not only 50%. In terms of the number of factorial combinations of key lengths, the 64-bit algorithm is 64,000 times more powerful than the 48-bit algorithm. Therefore, the 64-bit key is more difficult to crack. Designers should choose a label that provides an efficient and secure encryption algorithm with a key length of at least 64 bits. The security of an RFID tag can only be as high as the security of the tag reader that reads it. In other words, the 64-bit encryption algorithm on advanced RFID tags is only useful if the tag reader or host supports such 64-bit encryption algorithms. Like RFID tags, most tag readers on the market today only support minimal security and use old encryption algorithms and too short a key length, making them easy to crack. The new, more secure reader will support advanced military-grade 128-bit AES encryption algorithms while also supporting simpler encryption algorithms. They also allow password protection and allow for the use of optional encryption algorithms in multiple encryption zones on RFID tags. Vertical Mount Power D-SUB Connectors ANTENK launches series vertical board mount Power-D & Combo-D D-SUB connectors machined contacts.
Features of Vertical Mount D-SUB Connector Machined Contacts Male High Density Power D Mixed Contact Connectors, Female High Density Power D Mixed Contact Connectors, Male Standard Vertical Mount Power D-SUB Connector, Female Standard Vertical Mount Power D-SUB Connector ShenZhen Antenk Electronics Co,Ltd , https://www.antenkelec.com
The ANTENK Power-D & Combo-D mixed contact d-sub connectors straight are designed for rugged / robust applications where both power & signal are required from a single connection. Featuring [Solid-Pin" machined contacts, these connectors offer high reliability performance for the most challenging design applications.
vertical board mount Power-D & Combo-D D-SUB connectors machined contacts applications
The ANTENK vertical mount combo d-sub, mixed contact connector product range is ideal for a multitude of both IP rated and non-rated industry applications. This diverse combo d-sub standard product offering includes up to 13 contact configurations (seen below) engineered for both power & coaxial connector environments such as satellite & weather stations, GPS receivers, transceivers and radio technology applications. Contact us directly for any custom or semi-custom combo d-sub connector project not listed in our standard product offering above.
Available in 12 industry standard sizes / positions.
Contact Antenk for other sizes / contact configurations.
Available in 10/20/30/40 amp power contacts, 5 amp signal
Allows signal, high current & high voltage in one connector.
Contacts are pre-loaded into the insulator.
Material of Vertical Mount D-SUB Connector Machined Contacts
Shell: Steel, Nickel plated
Insulator: Glass-Filled Thermoplastic, U.L. 94V-O, Black
Signal Contacts: Machined Copper Alloy, Full Gold Flash
Power Contacts: Machined Copper Alloy, Full Gold Flash