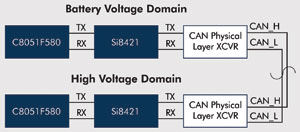
Mixed-signal microcontroller to enhance embedded system for vehicles By connecting different systems via the network to share information, monitor and increase safety, automotive-related applications are becoming increasingly sophisticated. As complexity increases, automotive systems need to use more effective electronic components to save space, which also means that there are fewer and fewer components on the printed circuit board (PCB), and semiconductor manufacturers must provide integration and performance Are stronger products, especially various microcontrollers (MCUs). Microcontrollers have been widely used in automotive equipment, and have been given a major responsibility for controlling more system functions and reducing circuit board space. The 8-bit mixed-signal microcontroller provides multiple ways to meet the designer's needs. The mixed-signal microcontroller eliminates the need for additional devices on the bill of materials (BOM) by adding hardware functions. The improved microcontroller can increase the speed, reduce the memory size and expand the periphery of the chip, and these must be completed in a very small area. As shown in Figure 1, using an integrated solution not only saves space, but also saves up to $ 0.70 in costs. This is because the use of mixed-signal microcontrollers can eliminate the use of external components, such as reference voltage sources, regulators, and resonators, thereby reducing board area. The more interconnected components on the printed circuit board, the more stability problems may often occur. Now, with fewer components required, stability can be greatly improved. Figure 1 Comparison of traditional system bill of materials (left) and highly integrated mixed-signal MCU (right) Another unique feature is that the integrated analog-to-digital converter is also an adjustable attenuator. This feature allows designers to dynamically attenuate the input signal to meet the voltage reference. This feature has the following two advantages. One is that all input signals higher than the reference voltage can use the full range of output codes, which means that the designer's signal will not be reduced, and all output codes can be fully utilized to the maximum dynamic range. The second is that this technology can be used to eliminate variations between sensors, such as calibration, and the resulting advantage is that designers can use lower-cost sensors to calibrate these sensors in the system. In this way, low-cost sensors can be used to achieve the same effect as expensive accurate sensors. The dedicated automotive serial bus also provides designers with advantages in terms of performance. For example, the CAN 2.0 engine, which provides 32 independent messages, can support a large amount of network traffic. By integrating a dedicated area network (LIN) 2.1 controller without LIN simulation by software, automotive designers can further enhance the design. 8 bytes of information buffering, hardware synchronization, and check code generation are done by hardware, which frees up more CPU resources and allows more complex LIN topologies. Another major consideration for designers of embedded devices in vehicles is "application flexibility". In the past, microcontrollers used fixed multi-tasking mechanisms, so designers were limited to selecting resources that match specific pins. Mixed-signal microcontrollers can use a crossbar switch matrix, which is a programmable switching structure, allowing designers to arrange digital peripherals on available I / O pins. This flexibility simplifies design time. An example of this is the ability to reuse resources. Designers can have two independent LIN buses and can dynamically remap and assign (re-map) pins during operation, which can save costs and give mixed-signal microcontrollers a unique flexibility. Another example is the use of vertical and horizontal matrices to reduce the cost of programming and calibration. Many designers must use a tester to calibrate the system at the end of printed circuit board assembly. At this stage, special calibration middleware can be programmed to interact with the tester The device, microcontroller resources can be used in the connection tester, thereby accelerating calibration and greatly reducing the overall test time. Once the system calibration is completed, the parameters are stored in non-volatile memory (NVM), and the device's middleware can also be programmed into the microcontroller. Figure 2 Eliminate the noise in the vehicle system From a design point of view, the digital isolator creates an isolation section between the CAN physical layer and the microcontroller running on the bus, which can isolate the effects of noise caused by common vehicle systems and further enhance performance. As shown in Figure 2, this is a good way to eliminate the ground loops that appear in automotive CAN and LIN, and is also suitable for applications in electronic noise environments.
The USB HUBS is also known as a port replicator which is an external device designed for laptop computers. By copying or even extending the port of the notebook computer, the notebook computer can be easily connected with multiple accessories or external devices (such as power adapter, network cable, mouse, external keyboard, printer and external monitor) in one stop.
Usb Hubs,Multi Usb Adapter,Usb C Desktop Hub,Usb 3.0 Multi Port Hub Henan Yijiao Trading Co., Ltd , https://www.yjusbhubs.com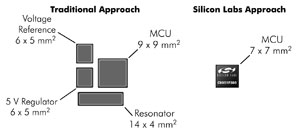
The USB C Hubs has both the functionality of a port replicator and is used to extend to a considerable degree of desktop functionality. Especially suitable for professionals, such as the need for more interface equipment. Using the laptop docking station for company, home or business presentations can also increase the ease of use and excellent scalability of the notebook. For example, consider using the UltraBay interface on the docking station to obtain an optical drive, burner, battery, numeric keypad, hard disk and other expansion functions.
The biggest use of the mini Type C Usb Hub is port expansion. As it is known to all, laptop computers are much less than desktop computers due to their own size limitations, both in terms of the number of ports and types, and sometimes it is difficult to meet the needs of users. The mini dock, on the other hand, offers multiple port extensions, like a laptop that suddenly has three heads and six arms. Some ports are most laptops do not have their own, such as serial port, PS/2, DVI, IBM dedicated floppy drive port. Some are more numerous than the body of a laptop, such as USB ports. These numerous ports allow the laptop to connect to more peripherals at the same time, improving the performance of the entire laptop and helping to increase productivity.
