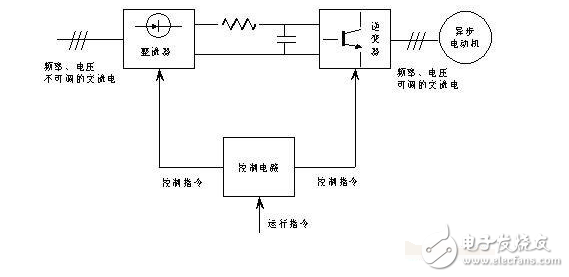
The AC-AC converter is also called a cycle converter. It is a process of converting the AC power of a fixed frequency of the power grid into a frequency-adjustable AC power directly through the power semiconductor circuit. It is different from the ordinary frequency converter, there is no AC rectification to DC and then inverter into AC, it is the structure of AC-AC conversion. This technology is generally used on large power devices. Variable-frequency drive (VFD) is a power control device that controls the AC motor by changing the working frequency of the motor by applying variable frequency technology and microelectronic technology. The frequency converter is mainly composed of rectification (AC to DC), filtering, inverter (DC to AC), braking unit, drive unit, and detection unit micro processing unit. The inverter adjusts the voltage and frequency of the output power supply by the internal IGBT breaking, and supplies the required power supply voltage according to the actual needs of the motor, thereby achieving the purpose of energy saving and speed regulation. In addition, the frequency converter has many protection functions. Such as overcurrent, overvoltage, overload protection and so on. With the continuous improvement of industrial automation, inverters have also been widely used. The working principle of the AC-DC converter is to rectify the power frequency power supply into a DC power by means of a microelectronic device, a power electronic device and a control technology, and then the DC power is inverted by the power electronic device into an AC power source with adjustable frequency. The schematic diagram of the AC-DC converter is as follows: As can be seen from the figure, the frequency converter is composed of a main circuit (including a rectifier, an intermediate DC link, an inverter) and a control loop. The functions of each part are as follows: 1. The function of the rectifier is to rectify the three-phase (or single-phase) AC power to DC. In SPWM inverters, full-wave rectifier circuits are mostly used. In most medium and small capacity inverters, the rectifier device uses an uncontrolled rectifier diode or diode module. 2. Inverter Its function is opposite to that of rectifier. It converts DC power into AC power with variable voltage and frequency to realize AC motor frequency control. The inverter circuit is composed of switching devices, and most of them use bridge circuits, which are often called inverter bridges. In the SPWM inverter, the switching device receives the control of the SPWM modulation signal in the control circuit, and inverts the direct current into three-phase alternating current. 3. Control circuit This part of the circuit consists of an arithmetic circuit, a detection circuit, a drive circuit, a protection circuit, etc., and generally uses a large-scale integrated circuit. The AC-DC converter is more common and consists of a rectifier, a filter system and an inverter. The rectifier is a full-controlled rectifier composed of a diode three-phase bridge uncontrolled rectifier or a high-power transistor. The inverter is a three-phase bridge circuit composed of high-power transistors. Its function is exactly opposite to that of the rectifier. It exchanges constant DC power to Adjustable voltage, adjustable frequency AC. The intermediate filtering step is to filter the rectified voltage or current with a capacitor or a reactor. AC-DC inverters can be divided into voltage type and current type according to different intermediate DC filter links. Voltage-type inverters are widely used due to various factors such as control methods and hardware design. It has applications in industrial automation inverters (using variable voltage variable frequency VVVF control, etc.) and IT, power supply uninterruptible power supplies (ie UPS, using constant voltage constant frequency CVCF control). Matrix Membrane Switch,Membrane Keypad Switch ,Prototype Membrane Switch,Keypad Membrane Switch CIXI MEMBRANE SWITCH FACTORY , https://www.cnjunma.com