China's optoelectronics industry has developed rapidly in recent years, growing at a rate of 30 to 40% per year. However, it currently accounts for only 5% of the global market and is expected to account for 10% of the global market by 2010. In addition, China's LED industry has also developed extremely rapidly. The output of high-brightness white-light GaN LEDs has grown at an annual rate of 59%. In 2006, the output was 7.2 billion, with a market size of 9 billion yuan. It is estimated that the output will reach 20 billion in 2010, which will surpass Japan to become the world's second largest producer. The simplest application of solar energy is to produce hot water, followed by electricity generation. An important application of power generation is lighting. China's lighting power accounts for 12% of the total electricity consumption. Due to the high cost of building large solar power plants and the large area of ​​high-power Solar Panels, the best way to achieve solar lighting is with light-emitting devices. Combined, they form a separate lighting device. At present, the most promising are solar street lights, solar garden lights, solar lawn lights, solar signal lights and solar beacon lights. Among them, solar LED street lights have the highest economic value. This is because ordinary street lamps need to be laid with long transmission lines. The laying of power lines requires a high cost, and as the distance increases, the voltage will gradually decrease, and the transformer will be boosted after a certain distance. Solar street lights are not the case. Since each street light pole is independent, there is no need to lay a transmission line, which greatly reduces the cost of erection. On the other hand, LEDs have much higher luminous efficiency than incandescent lamps, although they are numerically lower than high-pressure sodium lamps (high-pressure sodium lamps have a luminous efficiency of 132 lm/W and LEDs have only 70 lm/W), but the spectral dispersion of high-pressure sodium lamps A large part of it is in yellow, red and infrared, which has no effect on actual illumination, and a large part of the light is scattered in all directions. Therefore, from the actual road surface illumination effect (illuminance), the 150 watt LED is equivalent to a 400 watt high pressure sodium lamp. Assuming that the street lamp works 10 hours a day, then in 2 years, the 400 watt high pressure sodium lamp consumes 2920 kWh, while the 150 watt LED consumes only 1095 kWh, saving 2.66 times. In addition, LEDs have a long life and do not need to be replaced frequently. The life of a high-pressure sodium lamp is 4000 hours. Assuming that it works 10 hours a day, it can only work for 400 days, and it will be replaced more than a year. The life of a high-power LED is 50,000 hours. It is assumed that it will work 10 hours a day and will need to be replaced in 13.7 years. This greatly saves maintenance costs. Take the example of setting up 250 street lamps at a distance of 5 kilometers. The cost of cable laying, power distribution equipment and inspection wells for ordinary street lamps will cost 1.53 million yuan. The solar street lamp can save this cost; the electricity cost of the ordinary street lamp is also very considerable. In the above example, the ordinary street lamp needs to consume 5.475 million yuan in 15 years, and the solar street lamp only needs to replace the battery once, about 375,000 yuan. Moreover, the working voltage of the solar street lamp is low, and there is absolutely no electric shock accident. LEDs have a long life span and require almost no replacement for 15 years. On the one hand, they reduce maintenance costs and on the other hand reduce safety risks. Therefore, it is a street lamp with high cost performance. Solar garden lights and lawn lights have similar advantages, but because of the close distance and the small number, the advantages are not so significant. The United States reached 20 million LED streetlights in 2008. China had 15 million street lights in 2006 and is growing at a rate of 20% per year. The annual electricity bill for Chinese street lamps reaches 6 billion yuan, and all solar street lights can be saved. Solar lamps are composed of five parts: Solar Cells, batteries, control devices, LED driver chips and LEDs themselves. Usually, the solar panel is hung on the high pole, the charge and discharge controller and the lead storage battery are placed in the ground control box, and the driver chip and the LED are mounted in the lamp holder (as shown in FIG. 1). The charge and discharge controller can only control the charging and discharging process of the battery and supply power to the LED at a time, and cannot stabilize the output voltage thereof. However, many designers have omitted the constant current drive in their design. They think that the output voltage of the lead storage battery is stable enough, and it is not necessary to use a constant current drive to directly drive the LED. This idea is wrong. The output voltage of the battery will gradually decrease with discharge, and the output voltage changes up to about 20% during the entire discharge process. If you use it to directly power the LED, it will make a big difference in the brightness of the LED. Take the lead battery as an example, its discharge curve is shown in Figure 2. As can be seen from the figure, the output voltage of the lead storage battery will drop by 2V (nearly 20%) during the entire discharge process. From the volt-ampere characteristics of the LED, 20% of the voltage change will cause a great forward current change. Figure 3 shows the volt-ampere characteristics of a 3W LED, where blue is a white LED. 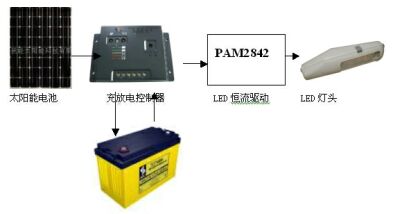
Figure 1: The solar luminaire consists of five parts. 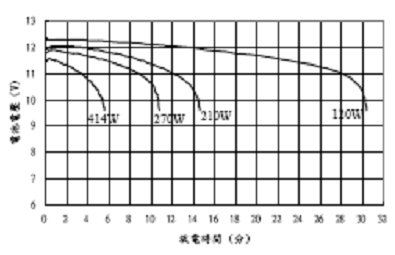
Figure 2: Discharge curve of lead storage battery. 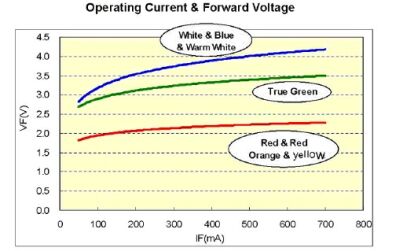
Figure 3: Volt-ampere characteristics of a 3W LED.