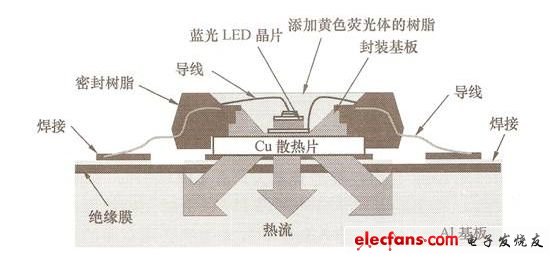
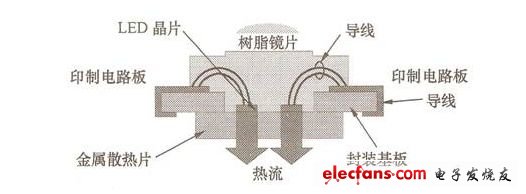
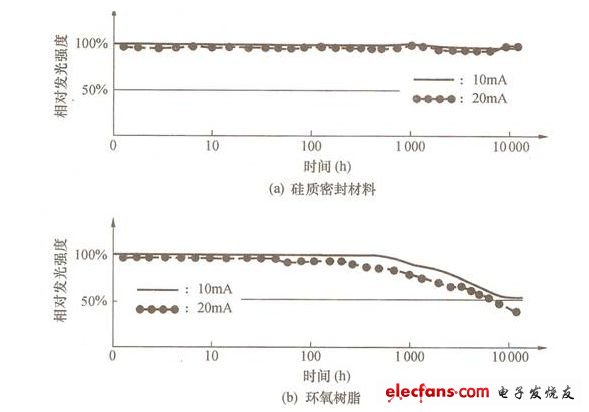
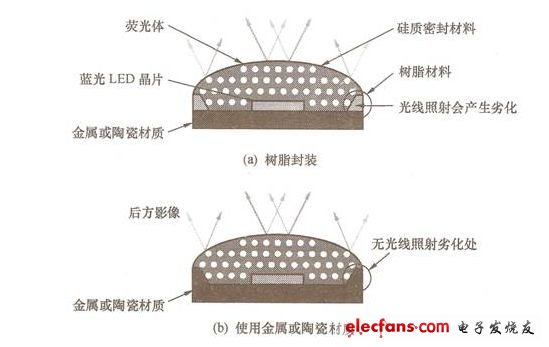
In order to obtain a sufficient white LED beam, large-size LED chips have been developed in an attempt to achieve the desired goal in this way. In fact, when the electric power applied to the white LED continues to exceed 1W, the beam will decrease, and the luminous efficiency will be relatively reduced by 20% to 30%. The problems that must be overcome to improve the input power and luminous efficiency of the white LED are: suppressing the temperature rise; Service life; improved luminous efficiency; equalization of luminescence characteristics. Increasing the power will reduce the thermal impedance of the white LED package to below 10K/W. Therefore, foreign countries have developed high-temperature resistant white LEDs in an attempt to improve the temperature rise problem. Since the heat of a high-power white LED is several times higher than that of a low-power white LED, even if the package of the white LED allows high heat, the allowable temperature of the white LED chip is constant. The specific way to suppress temperature rise is to reduce the thermal impedance of the package. The specific method to improve the life of white LEDs is to improve the shape of the chip, using small chips. Since the light-emitting spectrum of white LEDs contains short-wavelength light with a wavelength lower than 450 nm, the conventional epoxy resin sealing material is easily destroyed by short-wavelength light, and the large amount of high-power white LEDs accelerates the deterioration of the sealing material. Switching to siliceous sealing materials and ceramic packaging materials can increase the lifetime of white LEDs by one digit. The specific method for improving the luminous efficiency of white LEDs is to improve the chip structure and package structure to the same level as low-power white LEDs. The main reason is that when the current density is increased by more than 2 times, it is not easy to extract light from large chips, but the result will be The luminous efficiency is not as good as that of the low-power white LED. If the electrode structure of the chip is improved, the above-mentioned light extraction problem can be solved theoretically. A specific method for achieving uniformity of luminescent characteristics is to improve the packaging method of white LEDs. It is generally considered that the above problems can be overcome by improving the uniformity of the phosphor material concentration of the white LED and the fabrication technique of the phosphor. The specific contents of reducing thermal impedance and improving heat dissipation are: 1 Reduce the thermal impedance of the chip to the package. 2 Suppress the thermal impedance of the package to the printed circuit board. 3 Improve the heat dissipation of the chip. In order to reduce the thermal impedance, many foreign LED manufacturers set LED chips on the surface of heat-dissipating fins made of copper and ceramic materials. As shown in Figure 1, the heat-dissipating wires on the printed circuit board are connected by soldering to the cooling fan. Air-cooled fins. The experimental results of the OSRAM Opto Semiconductors Gmb in Germany confirmed that the thermal impedance of the LED chip to the solder joint of the above structure can be reduced by 9K/W, which is about 1/6 of that of the conventional LED. When the packaged LED applies 2 W of electric power, the temperature of the LED chip is 18 ° C higher than the solder joint. Even if the temperature of the printed circuit board rises to 500 ° C, the temperature of the LED chip is only about 700 ° C. Once the thermal impedance is reduced, the temperature of the LED chip is affected by the temperature of the printed circuit board. To this end, the thermal impedance of the LED chip to the solder joint must be reduced. Conversely, even if the white LED has a structure that suppresses the thermal impedance, if the heat cannot be conducted from the LED package to the printed circuit board, the rise in the LED temperature will cause the luminous efficiency to decrease, so Panasonic has developed a printed circuit board and Package integration technology, the company encapsulates a square blue LED with a side length of 1mm on a ceramic substrate in a chip-on-chip manner, and then pastes the ceramic substrate on the surface of a copper printed circuit board, including the printed circuit board. The overall thermal impedance is approximately 15K/W. (a) How to package OSRAM LEDs (b) CITIZEN LED packaging method Figure 1 LED heat dissipation structure In view of the longevity of white LEDs, the current measures taken by LED manufacturers are to change the sealing material and disperse the fluorescent material in the sealing material, which can more effectively suppress the deterioration of the material and the reduction of the light transmittance. Since the epoxy resin absorbs up to 45% of the wavelength of 400~450nm, the silicon sealing material is less than 1%, the brightness of the epoxy resin is reduced by less than 10,000 hours, and the silicon sealing material can be extended to 4 About 10,000 hours (as shown in Figure 2), almost the same as the design life of the lighting equipment, which means that the lighting equipment does not need to replace the white LED during use. However, the silicon sealing material is a highly elastic soft material, and must be used in processing. The manufacturing technique that scratches the surface of the silicon sealing material, and the silicon sealing material on the process are extremely easy to adhere to the dust, so it is necessary to develop a technology that can improve the surface characteristics in the future. Figure 2 Effect of silicon sealing material and epoxy resin on optical properties of LED Although the silicon sealing material can ensure that the white LED has a service life of 40,000 hours, the lighting industry has different opinions. The main argument is that the service life of traditional incandescent lamps and fluorescent lamps is defined as "the brightness is reduced to less than 30%", and the brightness is A white LED that has been halved for 40,000 hours, if it is converted to a brightness of less than 30%, only about 20,000 hours remain. There are currently two countermeasures to extend the life of the components: 1 Suppress the overall temperature rise of white LEDs. 2 Stop using the resin package. The above two measures can achieve the requirement of a service life of 40,000 hours when the brightness is reduced to 30%. To suppress the white LED temperature rise, the method of cooling the white LED to package the printed circuit board can be adopted. The main reason is that the encapsulating resin is rapidly degraded under the high temperature condition and the strong light irradiation, and the temperature is lowered by 100 ° C according to the Arrhenius rule. Will be extended by 2 times. Discontinuation of the resin package can completely eliminate the deterioration factor, because the light generated by the white LED is reflected in the encapsulation resin. If a resin reflective plate that changes the direction of the light on the side of the chip is used, since the reflection plate absorbs the light, the amount of light taken out will be Sharp reduction, which is the main reason for the use of ceramic and metal packaging materials. The resin-free structure of the LED package substrate is shown in Figure 3. Figure 3 LED package substrate without resin structure all in one computers, all in one desktops,all in one computer, all in one desktop,aio pc Guangdong Elieken Electronic Technology Co.,Ltd. , https://www.elieken.com