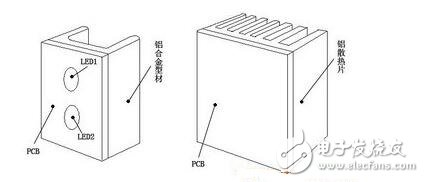
Here, part of the data of the NICHIA company's measurement TC is taken as a calculation example. The known conditions are as follows: LED: 3W white LED, model MCCW022, RJC=16°C/W. The K-type thermocouple point thermometer is welded to the cooling pad. PCB test board: double-layer copper plate (40 & TImes; 40mm), t = 1.6mm, weld surface copper layer area 1180mm2 back copper layer area 1600mm2. LED working status: IF=500mA, VF= 3.97V. According to Figure 9, the TC was measured with a K-type thermocouple thermometer, TC = 71 °C. The ambient temperature during testing was TA = 25 °C. TJ=RJC&TImes;PD+TC=RJC(IF&TImes;VF)+TC TJ=16°C/W (500mA&TImes; 3.97V) +71°C=103°C Figure 9 TC measurement position map RJA=(TC-TA)/PD = (71 ° C - 25 ° C) / 1.99 W =23.1 °C/W RJA=RJC+RBA =16°C/W+23.1°C/W =39.1°C/W If the designed TJmax=90°C, the TJ calculated according to the above conditions cannot meet the design requirements. It is necessary to change the better heat dissipation PCB or increase the heat dissipation area, and test and calculate again until TJ≤TJmax is satisfied. Another method is: when the RJC value of the LED used is too large, if the new similar product RJC=9°C/W (VF=3.65V at IF=500mA) is replaced, the other conditions are unchanged, and the TJ is calculated as: TJ=9°C/W (500mA×3.65V)+71°C =87.4°C There is some error in 71 °C in the above formula. A new 9 °C/W LED should be soldered to retest TC (the measured value is slightly smaller than 71 °C). This has little effect on the calculation. After adopting the LED of 9°C/W, the PCB material and area are not changed, and the TJ meets the design requirements. If the calculated TJ is much larger than the TJmax required by the design, and the structure is not allowed to increase the area, consider sticking the back of the PCB to the “∪†shaped aluminum profile (or aluminum plate stamping), or sticking On the heat sink, as shown in Figure 10. These two methods are commonly used in the design of luminaires for multiple high power LEDs. For example, in the above calculation example, a 10 ° C / W heat sink is attached to the back of the PCB where TJ = 103 ° C is calculated, and the TJ is lowered to about 80 ° C. Figure 10 “∪†shaped aluminum profiles It is to be noted that the above TC is measured at room temperature (room temperature is generally 15 to 30 ° C). If the ambient temperature TA used by the LED lamp is greater than room temperature, the actual TJ is higher than the TJ calculated after the room temperature measurement, so this factor should be considered in the design. If the test is carried out in an incubator, the temperature is adjusted to the highest ambient temperature during use, which is optimal. In addition, whether the PCB is mounted horizontally or vertically, its heat dissipation conditions are different, and it has a certain influence on the measurement of TC. The material and size of the casing of the lamp and the presence or absence of heat dissipation holes also have an effect on heat dissipation. Therefore, there is room for design. It is a simple and effective method to use the PCB with a certain heat dissipation area and the test board with LED to measure the TC recalculation under the working condition of the LED. It can be designed to meet the junction temperature TJmax requirement. Heat dissipation structure (PCB material and area). This heat dissipation design method is applicable to high-power LED lamps of other luminous colors, such as warning lights and decorative lights, in addition to lighting lamps for high-power white LEDs. In recent years, LED as a new energy-saving light source has won high investment enthusiasm and great attention in the world and China, and penetrated from the outdoor to the indoor lighting application market. China has also emerged tens of thousands of LED lighting companies. The main reason for letting LED lighting shine is its energy-saving, environmentally friendly, long-life, easy-to-control, maintenance-free features. However, it is ironic that we often hear that the LED lighting power supply itself directly drags down the LED lighting fixtures to become "longevity", which greatly increases the maintenance/use cost; or the efficiency of the driving power supply is not high, leading to LED lighting fixtures. The energy efficiency conversion ratio is not as high as imagined, or because the output current ripple is not well controlled, which affects the illumination quality, which makes the green energy-saving advantages of LED illumination greatly reduced, and even affects the market. 1. High reliability and longevity: The life of the driving power supply should be compatible with the life of the LED, especially for the driving power source like LED street light. Because it is installed at high altitude, the maintenance is inconvenient and the maintenance cost is also large; 2. High efficiency: This is especially important for structures where the power supply is installed in an LED luminaire. Since the luminous efficiency of the LED decreases as the temperature of the LED increases, the heat dissipation of the LED is very important. The power source has high efficiency, its power consumption is small, and the heat generated in the lamp is small, which reduces the temperature rise of the lamp, and is beneficial to delaying the light decay of the LED. 3. High power factor: With the increasing demands of the society for power quality, people are paying more and more attention to the power quality and harmonics caused by electrical equipment. If the European Union has issued standards, power supply devices with a power greater than 25W must have a power factor correction circuit. In many other countries, for 30 ~ 40W LED drive power, it is said that there will be certain indicators for power factor in the near future. 4. Constant current drive: There are two types of current traffic: one is a constant voltage source for multiple constant current sources, and each constant current source supplies power to each LED separately. This combination of flexible, one-way LED failure, does not affect the work of other LEDs, but the cost will be slightly higher. The other is direct constant current supply, with LEDs running in series or in parallel. Its advantage is that the cost is lower, but the flexibility is poor, and it is also necessary to solve the problem that one LED failure does not affect the operation of other LEDs. 5. Appropriate output ripple: Output ripple affects the LED's light output. But reducing ripple requires the use of higher quality and capacity capacitors. In order to improve the overall life of the power supply, designers tend to adopt a capacitorless solution. The engineer must determine the compromise on the output ripple indicator. 6. Surge protection: The ability of LED to resist surge is relatively poor, especially the ability to resist reverse voltage. Some LED lights are installed outdoors. Due to the start of the grid load and the detection of lightning strikes, various surges will be invaded from the grid system, and some surges will cause LED damage. Therefore, the LED driver power supply must have the ability to suppress the intrusion of surges and protect the LEDs from damage. 7. Protection function: In addition to the conventional protection function, it is better to increase the LED temperature negative feedback in the constant current output to prevent the LED temperature from being too high. 8. Protection: For the external installation structure of the lamp, the power supply structure should be waterproof and moisture-proof, and the outer casing should be light-resistant. 9. To comply with safety and electromagnetic compatibility requirements. people To achieve high-quality drive power design standards, a comprehensive test and measurement analysis is required. As shown in Figure 1, the LED lighting test consists of five parts: power quality, harmonics, power switching device measurement, modulation analysis, and drive output. Parametric test. Lens Caps,Lens Cover,Camera Lens Cover,Camera Lens Cap SHAOXING COLORBEE PLASTIC CO.,LTD , https://www.colorbeephoto.com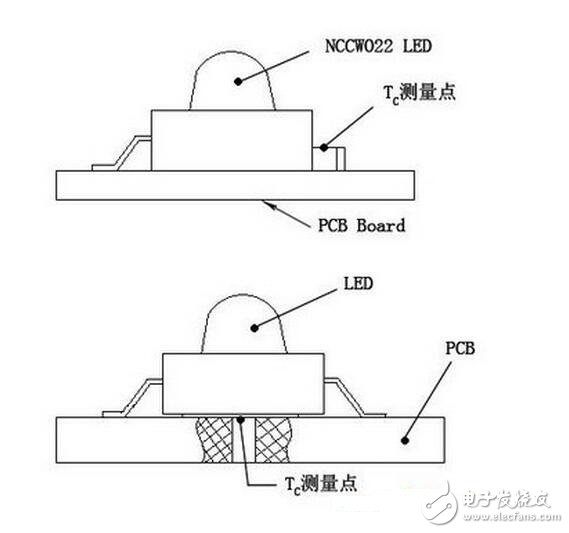






High-power LED heat treatment (attached), LED drive power implementation and design
How do high-power LEDs dissipate heat efficiently? Calculation example