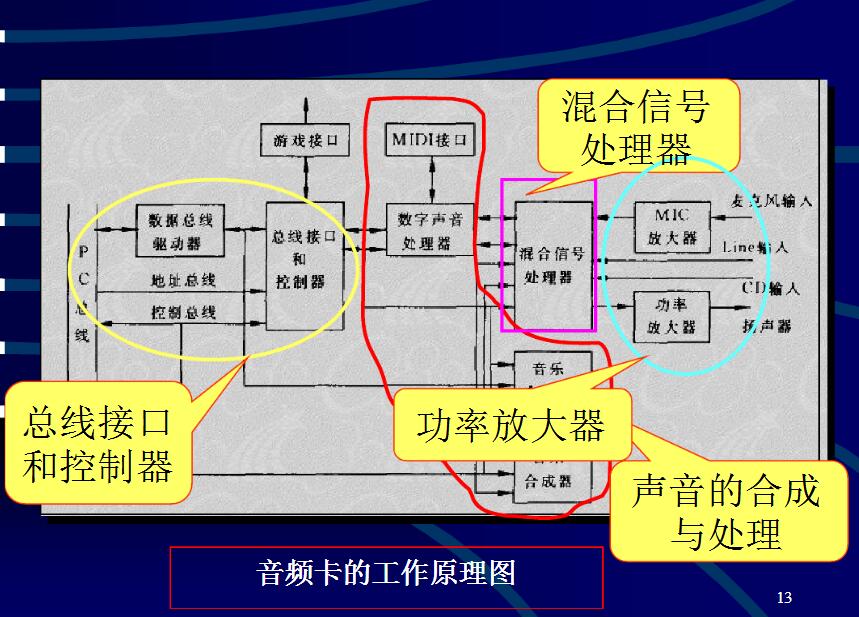
The audio card is the most basic component of multimedia technology and is a kind of hardware that realizes the mutual conversion of acoustic/digital signals. The basic function of an audio card is to convert raw sound signals from microphones, tapes, and optical discs to sound devices such as headphones, speakers, amplifiers, and tape recorders, or to make the instrument sound beautiful through the Music Device Digital Interface (MIDI). (1) Powerful audio processing engine (2) Environmental sound effects increase the content of existing audio (3) Sound Blaster PCI standard (4) Multi-speaker output, support 2 to 4 analog speakers, get surround sound effect (5) 256 polyphonic music synthesizer (6) Environmental sound function extension set / extensive software support (1) Synthesis and processing of sound This is the heart of the audio card, which consists of a digital sound processor, a frequency modulation (FM) music synthesizer, and a tone digital interface (MIDI) controller. The main task of this part is to complete the analog/digital (A/D) and digital/analog (D/A) conversion of the acoustic signal, and use the FM technology to control the pitch, tone and amplitude of the sound. (2) Mixed signal processor The mixed-signal processor has a built-in digital/analog mixer. The sound source of the mixer can be MIDI signal, CD audio, line input, microphone, etc. You can select a sound source or several different sound sources for mixed recording. (3) Power amplifier Since the signal power output by the mixed-signal processor is not large enough to drive the speaker or the speaker, it is generally necessary to have a power amplifier as the power amplification so that the output audio signal has sufficient power. (4) Bus interface and controller There are a variety of bus interfaces. The early audio cards were ISA bus interfaces. The current audio cards are generally PCI bus interfaces. The bus interface and controller consist of a data bus bidirectional driver, bus interface control logic, bus interrupt logic, and direct memory access (DMA) control logic. The classification of audio cards is mainly based on the number of bits quantized by the data samples, usually divided into: 8 bits, 16 bits, 32 bits. The higher the number of bits, the higher the quantization accuracy and the better the sound quality. (1) It can record digital sound files. Through the control of the sound card and the corresponding driver, the signals from the microphone, the recorder, etc. are collected, compressed and stored in the memory or hard disk of the computer system. (2) Restore the digital sound file compressed by the hard disk or the laser disk into a high-quality sound signal, and then zoom out and output through the speaker. (3) Processing digital sound files to achieve a specific audio effect (4) Control the volume of the sound source, combine various sound sources to realize the function of the reverberator (5) Using language synthesis technology to read text information through a sound card. Such as reading English words and sentences, playing music, etc. (6) has a preliminary audio recognition function, allowing the operator to command the computer to work with a password (7) Provide MIDI function, so that the computer can control multiple electronic instruments with MIDI interface. In addition, under the action of the driver, the sound card can output the files stored in the MIDI format to the corresponding electronic musical instruments, and emit corresponding sounds. Make the electronic musical instrument under the command of the sound card. 1. MME (MultiMedia Extensions Multimedia Extension) The lower level driver was first introduced in the Windows 3.1 era. Due to the long waiting time, sequence software such as Cubase VST and Logic Audo should be avoided unless a replacement is found. However, its use in Cakewalk Sonar seems to have excellent performance, and MME also has quite good performance when used by some independent software synthesizers. 2, DirectSound It generally provides latency much lower than the MME, and is suitable for many software synthesizers (if a dedicated driver is missing), which has the additional advantage of being able to be used simultaneously by multiple programs. DirectSound is hooked to the Windows base layer and can use the various acceleration features of the motherboard, but it must have a corresponding driver. Otherwise, although Windows has chosen DirectSound on its surface, it actually uses the imitation mode, and the performance aspect can be even worse than the MME. The main limitation of DirectSound is that it only works for playback. If your work includes recording, you should choose another driver. 3, ASIO (Audio Stream Input Output audio stream input and output) Going to the world with Steinberg's popular MIDI plus audio software, Cubase VST, is a driver that really provides low latency of less than 10 milliseconds. ASIO 2.0 supports multiple port (via ADAT) sampling precision addressing and zero wait listening. If your sequencer and sound card both support ASIO, consider using it first. 4, EASI (Enhanced Audio Streaming Interface enhanced audio stream interface) The performance is better than ASIO for drivers that are only used by a few sound cards. The CPU usage is significantly lower than ASIO when running Emagic Logic Audio after version 4.0. So for Logic Audio users, EASI is always preferred. Although Logic Audio uses ASIO, it is generally good. 5, GSIF (GigaSampler Interface Giga sampler interface) Works only on the Tascam/Nemesys Gigasampler and GigaStudio series software samplers, with a high quality sound library, fixed low latency (6 to 9 milliseconds). If you use these software, GSIF support is probably essential. Although the DirectSound driver works on a limited occasion, it has a much longer wait time and does not support multiple output ports. If there is no problem with the sound card, Giga products are always driven by GSIF. 6, WDM (Win32 Driver Model 32-bit Win driver module) Microsoft's newer type of driver, the first option as Windows 98 SE (there were some problems at the time, a few manufacturers therefore launched their own drivers), they can successfully run on Windows ME, of course, more significant is for Windows 2000 and XP users. They offer much lower latency than MME or DirectSound drivers (in some cases an amazing 1.5 milliseconds). They tend to be launched later than the operating system and will improve somewhat in the future. If you run Sonar under Windows 2000 and XP, WDM is a must. Turbocharger For Gas Generator Turbocharger For Gas Generator,Engine Turbocharger,Turbocharger For Generator,Turbocharger For Marine Engine Jinan Guohua Green Power Equipment Co.,Ltd. , https://www.guohuagenerator.com



A text to understand the working principle and main features of the audio card
What is an audio card?